CRC2 is Chromia’s upcoming NFT standard, designed to be interoperable with both ERC-721 and ERC-1155 while offering enhancements like metadata expansion, on-chain content storage, and built-in programmability.
While CRC2 is new, it builds on ideas first explored under the name Chromia Originals. In many ways, CRC2 is a spiritual successor to Originals, as it incorporates many of the same ideas and end goals.
Q3 will bring the public release of CRC2, an EVM-compatible bridge, and supporting documentation, opening the door to adoption and creative implementations of NFTs on Chromia. In advance of this release, let's take a closer look at how NFTs work and explore what CRC2 brings to the table.
How Do ERC-721 NFTs Work?
The majority of NFTs today use the ERC-721 standard, which was originally developed on Ethereum. This standard has in turn been adopted by EVM-based Layer-1 and Layer-2 networks like Binance Chain, Base, Polygon, and others.
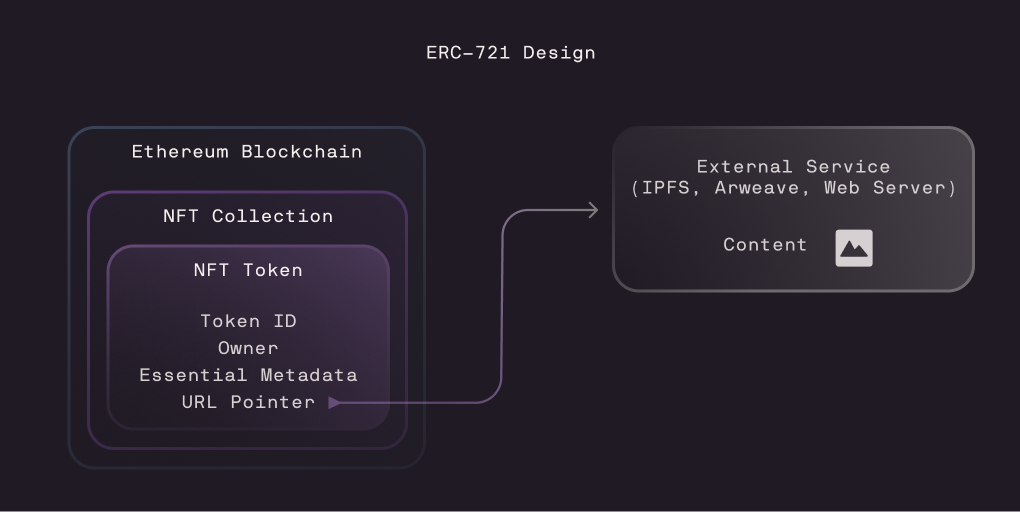
One thing that often surprises people new to NFTs is that these tokens usually don’t actually contain the images or other content associated with them. Instead, the token stores text-based metadata that contains essential information about the token and includes a link to an external location where the actual content (images, videos, music, or other data) is stored. The primary reason for this design is cost. On Ethereum, more data means more block space used and higher gas fees.
Creators of EVM-based collections must choose how and where to store their content. This decision affects the long-term accessibility and reliability of the NFT.
Some opt for more robust solutions like the IPFS peer-to-peer storage network, or Arweave, a blockchain-based storage protocol. These options are preferable, as they reduce the risk of content disappearing over time.
However, some collections store their content on privately hosted web servers, a more fragile setup. If the servers become inaccessible for any reason, the associated content can disappear completely.
No matter the method, there is always an external dependency and NFT holders are ultimately bound to the decisions made by the collection’s creator.
CRC2 Design
CRC2’s core design principle is modularity. It allows developers to start with a simple “base case” NFT that provides a familiar foundation. From there, projects can expand functionality as needed, making the protocol both accessible and highly adaptable.
Developers can choose from pre-existing modules to add new capabilities or build their own custom functionalities to meet specific needs. This approach allows projects to scale from simple, static NFTs to advanced tokens with dynamic behaviors and specialized features.
The standard is interoperable with ERC-721 and ERC-1155, while also supporting expanded metadata storage, greater programmability, and the option to store content (images, GIFs, audio, video etc.) directly on Chromia using Filehub. When this method is used, the NFT becomes self contained on-chain, with no reliance on external hosting.
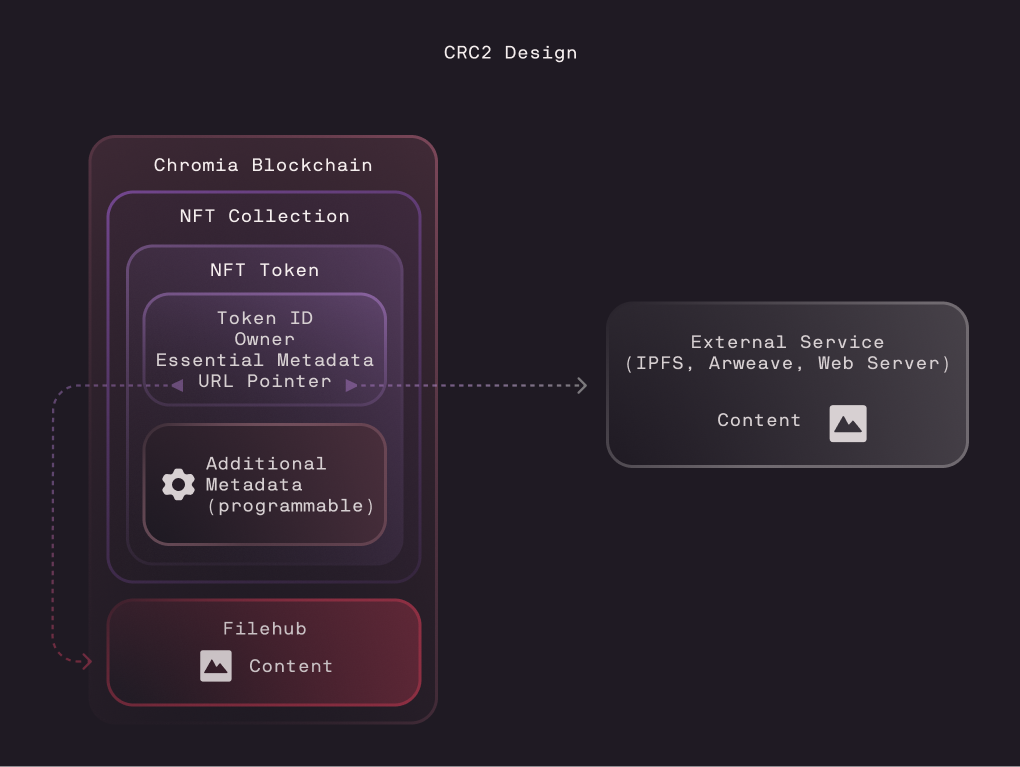
What Does Programmable Mean?
In the graphics, you’ll notice a section labeled “Additional Metadata (programmable).” While it may seem like a small detail, this feature unlocks a range of possibilities that aren’t achievable with standard NFT formats on other blockchains.
With CRC2, developers can define not just static metadata, but also embed logic and behaviors directly into the token. This means NFTs can be programmed to evolve, respond to user interactions, and integrate deeply with applications and games. For example:
- An NFT could level up over time, based on its age, user activity, or milestones reached within a game or dapp.
- Multiple NFTs could be combined to create something new, enabling mechanics like crafting.
- Tokens could have built-in usage limits, automatically deactivating or “self-destructing” after a set number of interactions.
This programmability makes CRC2 NFTs highly flexible and adaptable. Rather than being limited to fixed attributes, developers can build tokens that serve specific functions and evolve with the applications they’re part of. In short, CRC2 gives creators the tools to design NFTs that go beyond static collectibles.
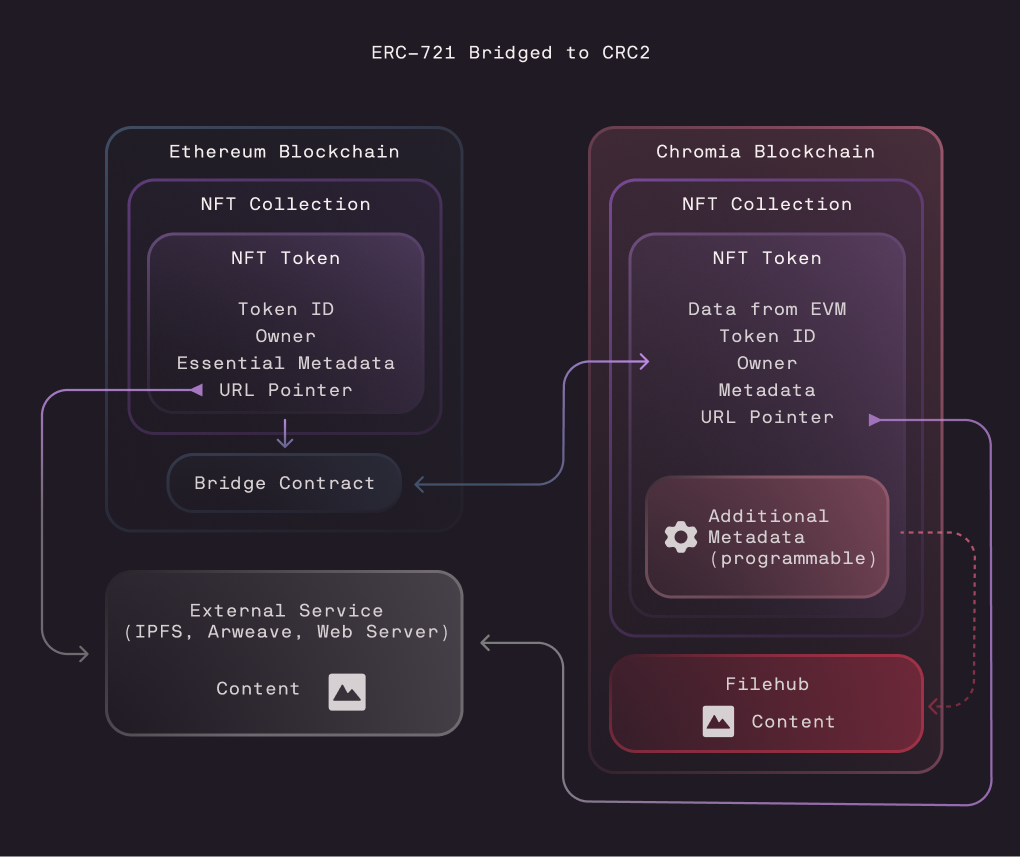
Bridging Existing NFTs from EVM Chains to Chromia
The design of CRC2 allows it to be interoperable with ERC-721 and ERC-1155, making it possible for EVM-based NFTs to be bridged to Chromia. Once bridged, these tokens can be enhanced with additional metadata, programmability, and on-chain content that go beyond the limitations of their original format.
When an NFT is bridged, the original token is locked in a holding contract on its native EVM chain. A corresponding CRC2 token is then created on Chromia, preserving the essential information from the original NFT. This bridged version retains the identity of the original token while gaining access to CRC2’s expanded features, such as extra metadata fields and the ability to link or store rich content directly on the Chromia blockchain.
Ownership is securely maintained throughout the bridging process. For example, if you transferred the NFT to another Chromia account, only the new owner would be able to bridge it back to Ethereum. In that case, the bridge contract on Ethereum would release the token to their address.
While the additional data on Chromia does not transfer back to EVM, it remains preserved. If the NFT is later bridged back, Chromia will still have this extra data and recognize that it belongs to that specific NFT.
This bridging mechanism enables developers and creators to take existing NFTs and upgrade them with new capabilities, without losing compatibility or ownership guarantees on the original chain.
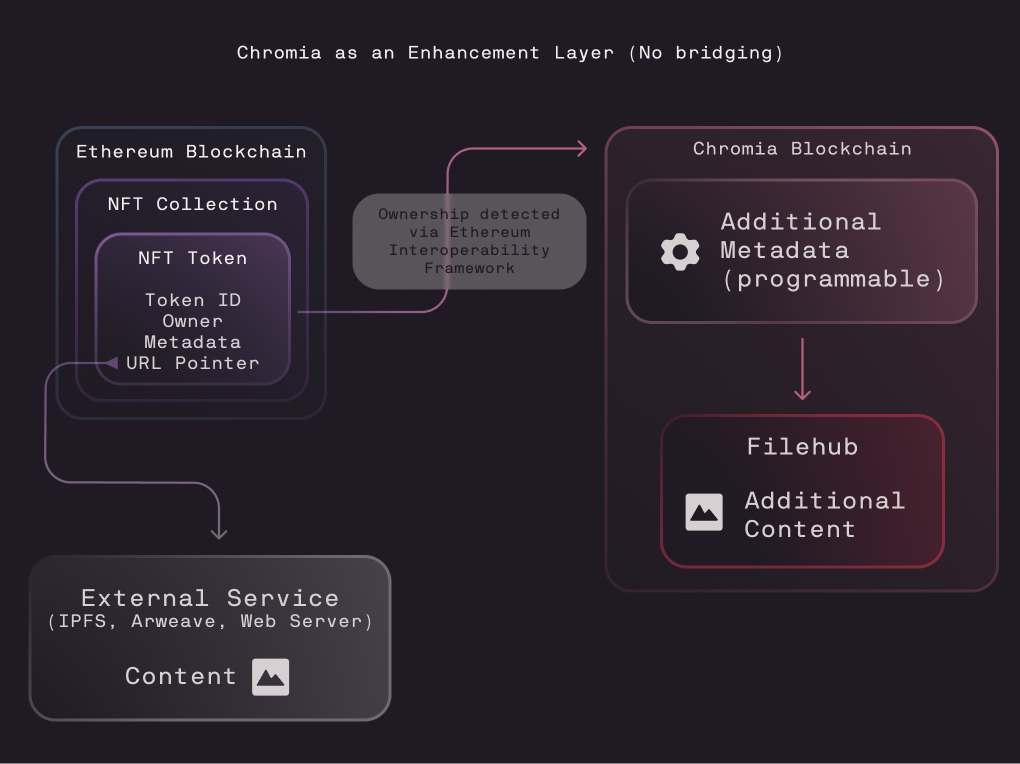
Using Chromia as an Enhancement Layer for Existing NFTs
Also worth exploring is how Chromia can serve as an enhancement layer for existing NFTs without the need for bridging.
Instead of moving an NFT away from its original chain, developers can reference it on Chromia and build a parallel metadata layer that adds depth, interactivity, and context. This approach preserves the original token’s provenance while enabling entirely new capabilities, such as custom traits, behavioral logic, progression histories, and user-driven interactions.
An early example of this concept is our Social Agents demo, which lets users assign personalities, behaviors, and relationships to Ethereum-based NFTs. There’s no bridging or modification of the original asset because the NFT remains on its native chain, while Chromia provides an additional logic and metadata layer that brings it to life.
Looking ahead, we are exploring ways to align this functionality with CRC2. One possibility is allowing enhancement layers to be created in advance, so that if an NFT is later bridged to Chromia, the CRC2 token can automatically inherit the existing additional content. This would create a seamless path EVM to Chromia and give creators and owners flexibility now, and powerful enhancement options later.
A New Era for NFTs on Chromia
CRC2 marks a key advancement for NFTs on Chromia, combining EVM interoperability with advanced features like expanded metadata, on-chain content storage, and programmability. As it approaches full public release, CRC2 is set to open new opportunities for creators, developers, and users.
The future of NFTs on Chromia goes beyond simple ownership to enable dynamic digital assets that evolve and interact within a connected blockchain ecosystem. As always, keep up to date on the latest development and ecosystem news by following our social media channels!
About Chromia
Chromia is a Layer-1 relational blockchain platform that uses a modular framework to empower users and developers with dedicated dapp chains, customizable fee structures, and enhanced digital assets. By fundamentally changing how information is structured on the blockchain, Chromia provides natively queryable data indexed in real-time, challenging the status quo to deliver innovations that will streamline the end-user experience and facilitate new Web3 business models.
Website | X | Telegram | Instagram | Youtube | Discord | Reddit | LinkedIn | Facebook |
